
The spike in inflation we’ve seen this year has impacts beyond having to pay more for goods and services. The IRS uses consumer price inflation (CPI) to determine certain increases to exemptions and deductions for federal tax purposes. These are automatic and calculated from the rise in CPI.
That means that the increased inflation this year may actually end up saving you money.
While the changes are for 2022 and you won’t be paying the associated taxes until 2023, it’s a good idea to be aware of the new limits.
You may be able to make changes as you go that can help you maximize the benefit.
For example, the amounts for Flexible Spending Accounts (FSAs) and the commuter benefit increased. You may want to have more taken out of your paycheck to reflect this change. This saves you money by paying with pre-tax dollars for expenses you’re likely to pay anyways.
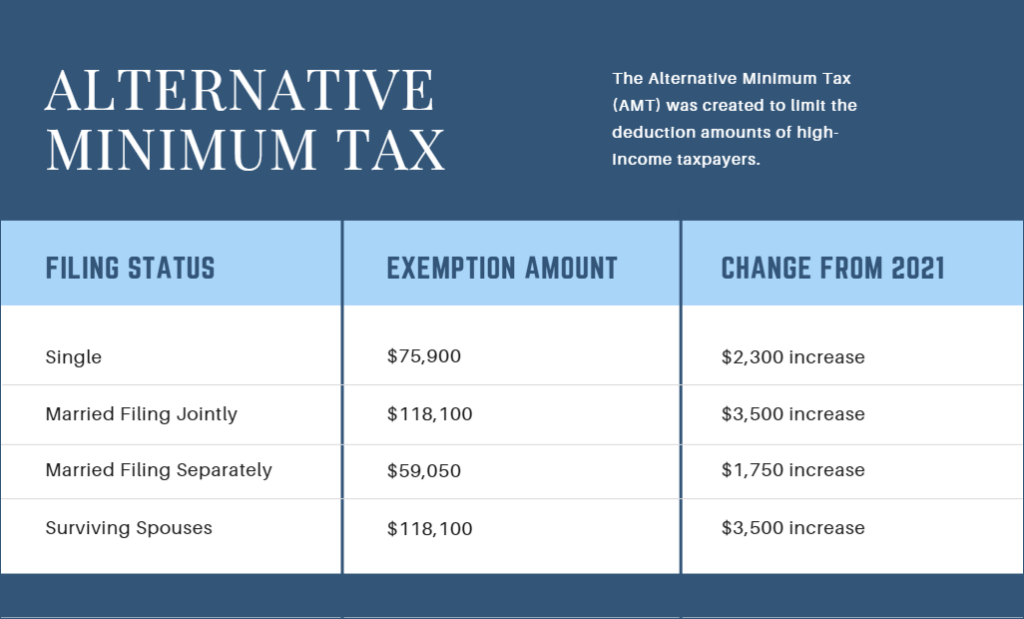
The income levels at which AMT applies also went up. If you have stock options, AMT very often comes into play. The increase amounts to $2,300 over the 2021 level for a single filer. While it doesn’t seem like much, it may be enough to allow you some flexibility in structuring them that will save you on taxes.
As always, we are not tax advisors. Please consult your tax professional on how these changes may affect your individual situation.
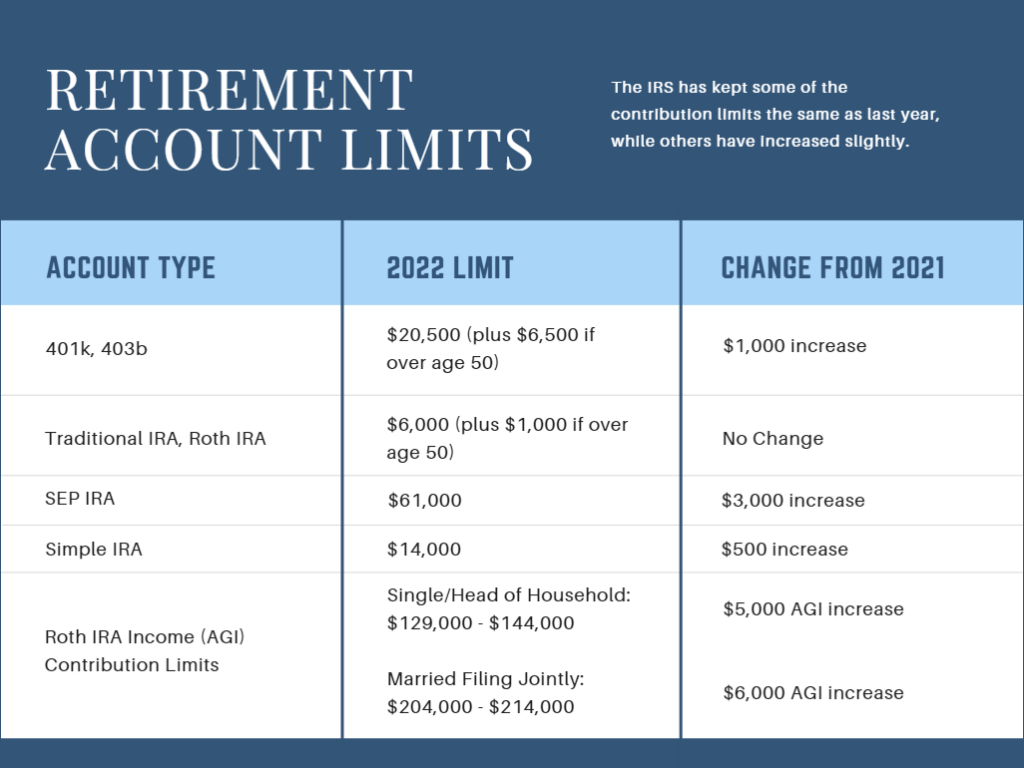
Retirement Contribution Limits
For workplace retirement accounts (i.e. 401(k), 403(b), amongst others), the contribution limit rises $1,000 to $20,500. Catch-up contributions remain at $6,500.1
Eligibility for Roth IRA contributions has increased, as well. These have bumped up to $129,000 to $144,000 for single filers and heads of households, and $204,000 to $214,000 for those filing jointly as married couples.1
Another increase was for SIMPLE IRA Plans (SIMPLE is an acronym for Savings Incentive Match Plan for Employees), which increases from $13,500 to $14,000.1
Unfortunately, not everything changes in 2022.
Traditional Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs), with the limit remaining at $6,000. The catch-up contribution for traditional IRAs remains $1,000 as well.1
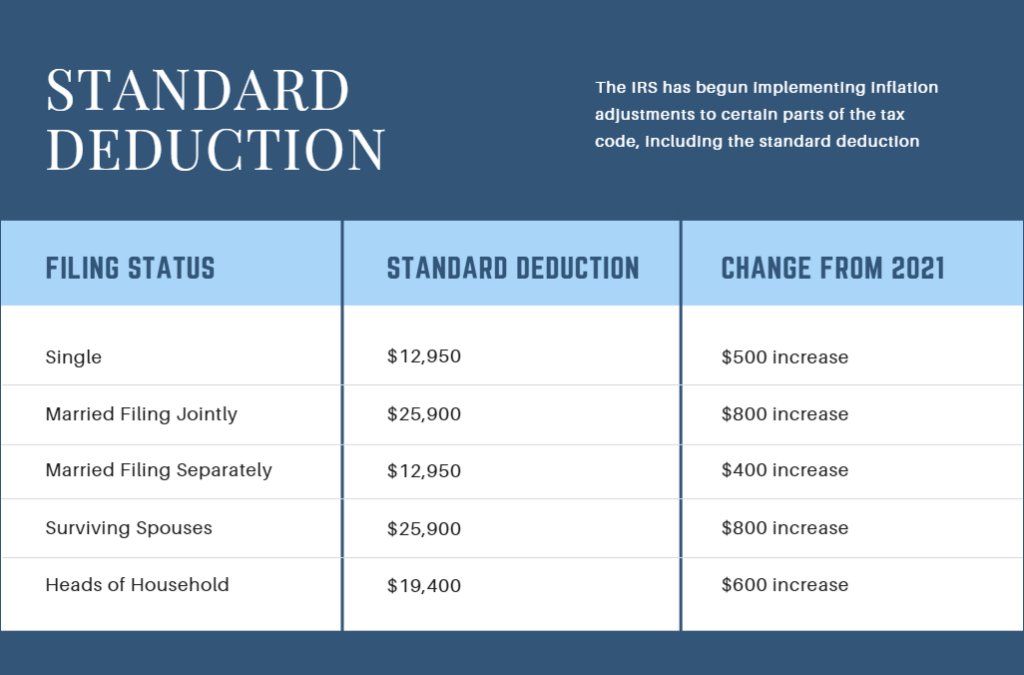
Taking the Standard Deduction
The standard deduction increased in 2018, and many taxpayers now opt not to itemize. For 2022, this choice becomes even more attractive as the deduction for a married couple filing jointly increased by $800. Taking the standard deduction simplifies tax preparation, but if you have deductible expenses such as medical expenses, property taxes, mortgage interest, charitable giving, or others (and there are hundreds), you may be passing up tax savings.
If your total itemized deductions are close to the amount of the standard deduction, there are strategies for charitable giving that can increase your tax deductions in any one year. This can be done without increasing your overall plans for giving. Giving some thought to your deductions as you move through the year can help you keep track of where you want to be.
Alternative Minimum Tax
The alternative minimum tax was created to limit the amount that high-income taxpayers can lower tax amounts through deductions or credits. It sets a floor on the amount of tax that must be paid. The AMT is particularly relevant if you have been granted incentive stock options (ISOs) as part of your compensation.
The AMT is adjusted based on the price you pay for the shares (the strike price) and the fair market value when you exercise. Because you can choose when to exercise, you have some flexibility in avoiding or minimizing AMT, but it requires careful planning of your income.
Flexible Spending Accounts and Commuter Benefits
The dollar limit for 2022 contributions to a flexible savings account is $2,850, an increase of $100 over 2021. If your plan allows carryovers, the new carryover limit is $570.
The monthly commuter benefit contribution limit for 2022 to your qualified parking and transit accounts increased to $280.
Gift and Estate Tax Exclusions
The annual federal exclusion for gifts was bumped up $1,000 to $16,000 for 2022. For a married couple, this means they can gift $32,000 to any individual without using their lifetime exemption.
The lifetime exemption also went up, to $12.06 million per person.
The Takeaway
Increases in deductions and exemptions are one of the few areas that inflation can help out investors – but you’ll need to plan ahead to take advantage of some of the increases.
There are lot of moving parts to a comprehensive plan that can save you money on taxes, and it’s never too early to get started in making the right moves.
1. CNBC.com, Friday, November 5, 2021
The information contained herein is intended to be used for educational purposes only and is not exhaustive. Diversification and/or any strategy that may be discussed does not guarantee against investment losses but are intended to help manage risk and return. If applicable, historical discussions and/or opinions are not predictive of future events. The content is presented in good faith and has been drawn from sources believed to be reliable. The content is not intended to be legal, tax or financial advice. Please consult a legal, tax or financial professional for information specific to your individual situation.
Once you reach age 72, you must begin taking required minimum distributions from a Traditional Individual Retirement Account (IRA) or Savings Incentive Match Plan for Employees IRA in most circumstances. Withdrawals from Traditional IRAs are taxed as ordinary income and, if taken before age 59½, may be subject to a 10% federal income tax penalty. Once you reach age 72, you must begin taking required minimum distributions from your 401(k), 403(b), or other defined-contribution plans in most circumstances. Withdrawals from your 401(k) or other defined-contribution plans are taxed as ordinary income and, if taken before age 59½, may be subject to a 10% federal income tax penalty. To qualify for the tax-free and penalty-free withdrawal of earnings, Roth IRA distributions must meet a five-year holding requirement and occur after age 59½. Tax-free and penalty-free withdrawal can also be taken under certain other circumstances, such as the owner’s death. The original Roth IRA owner is not required to take minimum annual withdrawals. The content is developed from sources believed to be providing accurate information. The information in this material is not intended as tax or legal advice. Please consult legal or tax professionals for specific information regarding your individual situation. This material was developed and produced by FMG Suite to provide information on a topic that may be of interest. FMG Suite, LLC, is not affiliated with the named representative, broker-dealer, state- or SEC-registered investment advisory firm. The opinions expressed and material provided are for general information and should not be considered a solicitation for the purchase or sale of any security.
